- We discuss properties of components.
- We study how to compose simple components to construct complex components.
- We study operations: renaming, parallel composition, and output hiding.
- We introduce the notion of task graphs.
- We illustrate the applicability of the synchronous model by designing synchronous circuits and a cruise controller.
Exercise 1
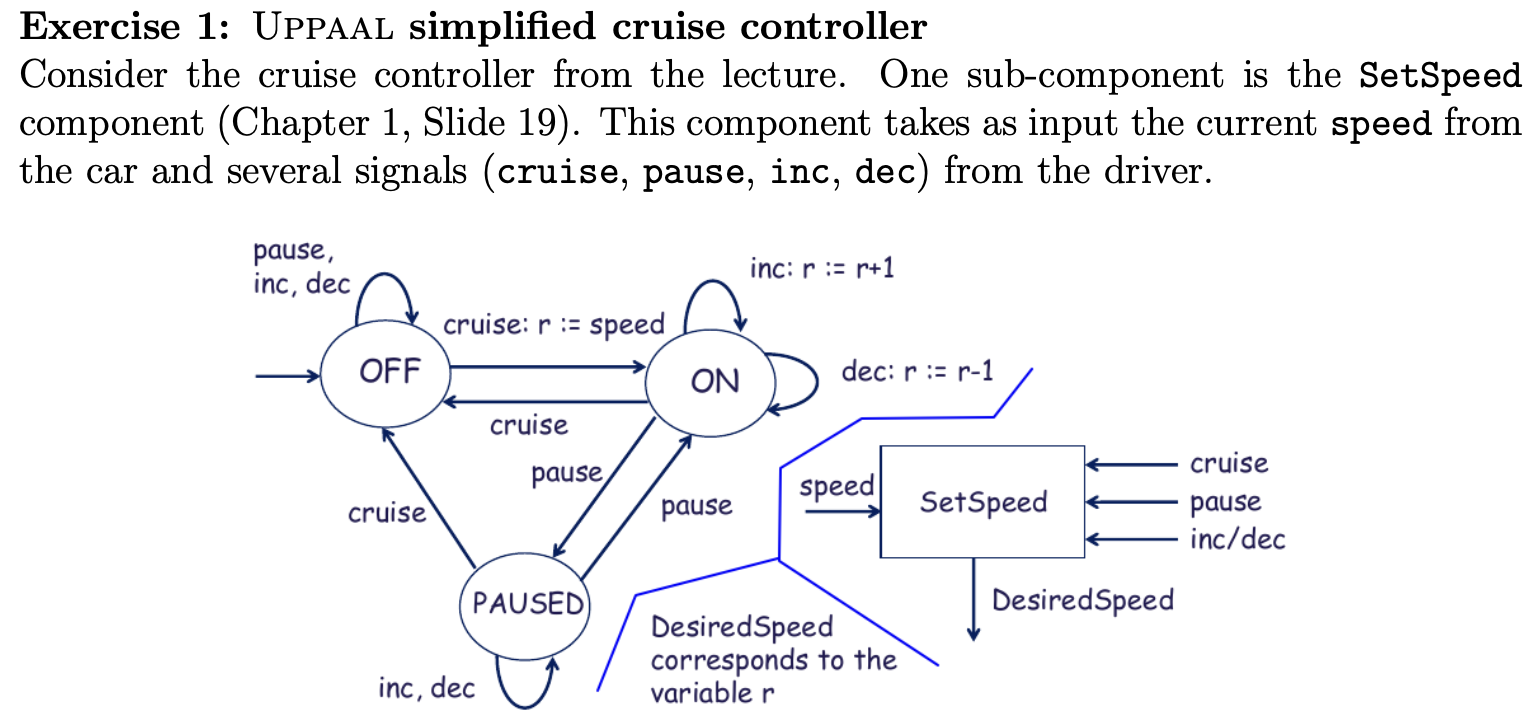
a) Done b) so we set our queary(s) to this to check if it ever goes over or under the values set here. A[] desired_speed >= 40 A[] desired_speed ⇐ 80 and it does not pass
c) There are probably multiple ways of doing this, but changing the Declarations of netspeed solves the issue easily.
int decrease_speed(int s) {
if ( s > MIN_SPEED ) // Set the proper bound for our lowest speed.
s--;
return s;
}
int increase_speed(int s) {
if ( s < MAX_SPEED ) // Set the proper bound to the max speed.
s++;
return s;
}Exercise 2
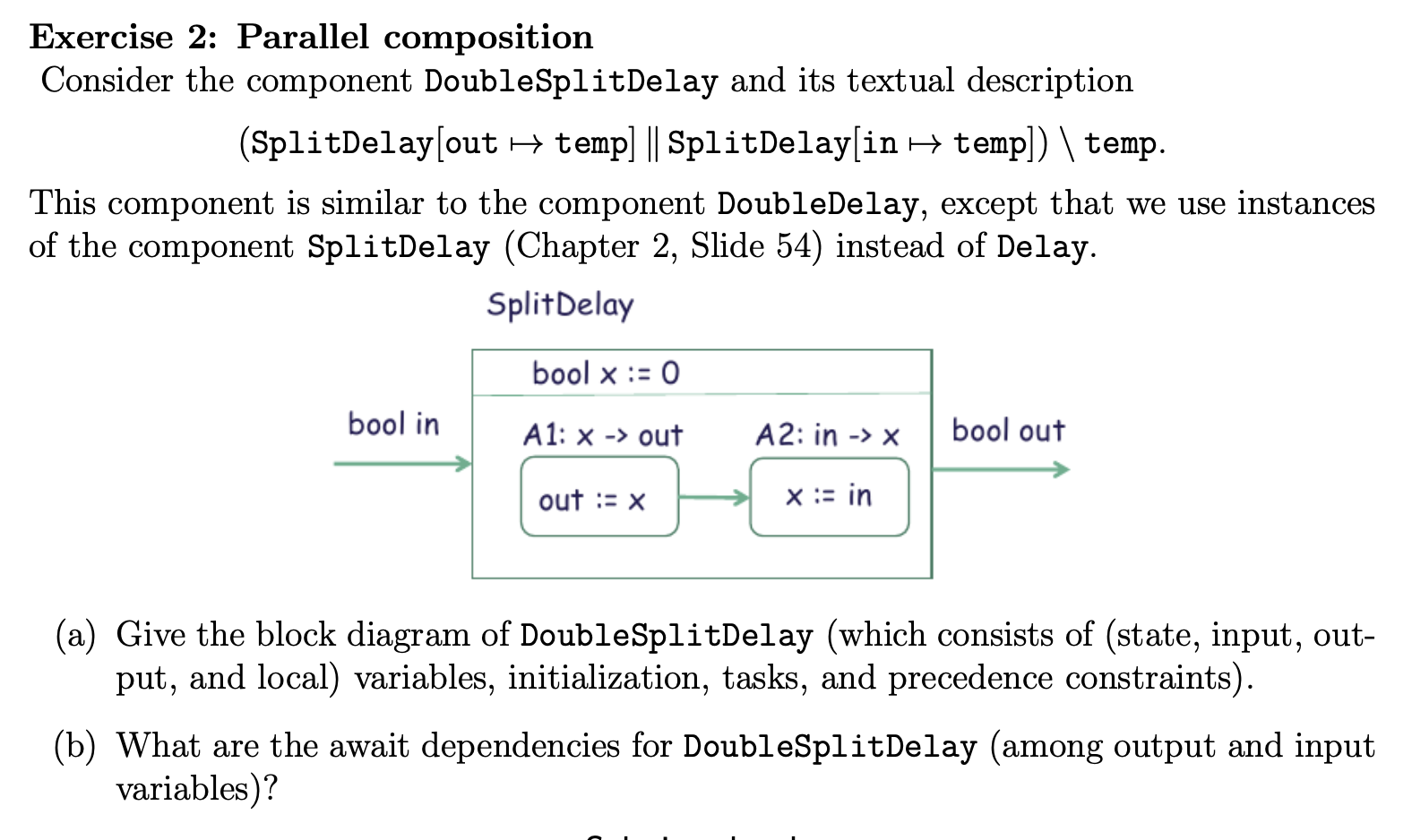 essentially what we need to do here is to double up the split delay so it holds on to it one longer.
essentially what we need to do here is to double up the split delay so it holds on to it one longer.
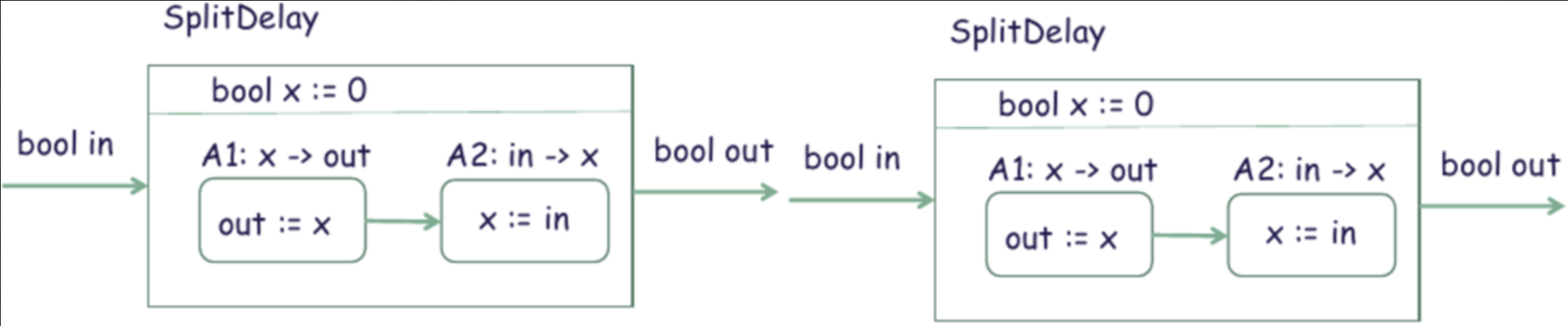
and in practice it would look something like this.
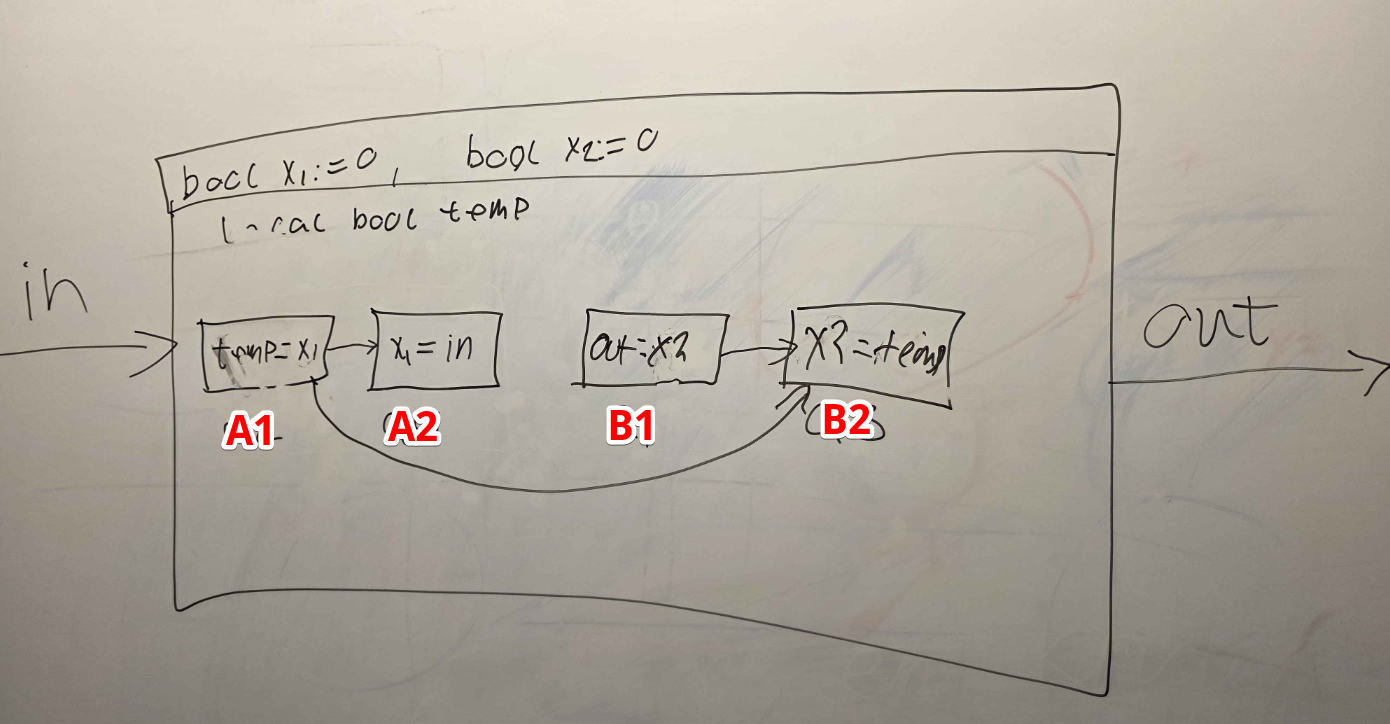

A1: out = x2 A2: x2 = x1 A3: x1 = in The above order also seems to be valid?
Exercise 3
The only intricate aspect is the substitution. We first have to rename minute to hour before we can rename second to minute.
(SecondToMinute || SecondToMinute[minute -> hour][second -> minute]) \ minute